Everything you need to know about South Dakota child support laws, updated for 2020.
South Dakota child support laws function on the premise that every child needs financial and emotional support from both parents.
That means the law requires you and your partner, whether married or unmarried, to cater to your child’s needs until he or she attains the age of majority. But… and that is a big one. Divorce, separation, or a child born out-of-wedlock does not automatically result in -Child Support Obligation. So, we ask, how is paternity established in South Dakota?
Is it possible to end child support before the child is 18?
What can you do if your support order is unfair? Find all the answers below.
How to apply for child support in South Dakota?
In South Dakota, the Division of Child Support Services/DCS provides child welfare facilities including, non-custodial parent location, paternity and order establishment, and child support enforcement.
To apply for services in the state, you must first download and complete DSS-SE-408CP/RA (07/2019) Application for Support Services Form. The three-page application includes details such as your parental responsibilities and accounting procedures. Therefore, read the instructions before you complete it.
What to remember:
- Parents not receiving public assistance must pay a $5 service fee.
- You can contact the DCS via this number 605-773-3641.
- The DCS only enforces health insurance if the courts ordered the payor to provide cover (And Insurance is available through employment).
- The DCS does not provide divorce assistance, legal advice, or counsel, nor alimony order establishment.
- Caregivers receiving TANF, Medicaid, Title IV-E foster care, and so on qualify for DCS services without application.
- The DCS charges a $20 fee for parental location services. Furthermore, the income withholding fee is $25, and $50 for parental kidnapping cases.
How is paternity established in South Dakota?
In South Dakota, when a child is born to a married couple, the law assumes that the man is the father until proven otherwise. But South Dakota child support laws also recognize that not all parents in the state are willing to own up to their parental responsibilities. That is why there are two ways to establish paternity in South Dakota.
The first option is voluntary establishment, whereby a man signs the ‘paternity Affidavit Form’ at the hospital or in front of a notary. Whereas, involuntary establishment happens after one parent files a “petition to establish paternity” at the local circuit court or after the DSS (Division for Support Services) gets a court order requiring the parent to take a paternity test.
What to remember:
- Signing a Paternity Affidavit Form at the hospital-automatically makes you the father.
- If either parent denies paternity, the other parent can petition the court or DSS to order DNA testing.
- You may obtain the Paternity Affidavit Form at the hospital, Department of Social Services, local register of deeds office, or at the Department of Health offices.
How is child support determined in South Dakota?
The two main ways to calculate, or rather, to estimate Child Support Obligation in south Dakota are; one, use the DSS provided child support calculator that is based on South Dakota child support laws. Or two, you may opt to use Dakota child support worksheets. What do I mean?
First, the calculator can only estimate, meaning your order may be very different from the estimate you get using the calculator or worksheet. Two, the judge awards upkeep amounts based on the best interests of the child. Hence, if the resulting amount does not capture the needs of the child, then the court may deviate from south Dakota child support laws.
South Dakota’s version of the incomes share method
South Dakota is one of the many states that use the income shares method in distributing support obligations. What that means is, the courts use economic tables/Schedule of Basic Obligation to estimate the total cost of raising a child in the state.
How to calculate child support in South Dakota
Therefore, to estimate child support, here is what to do.
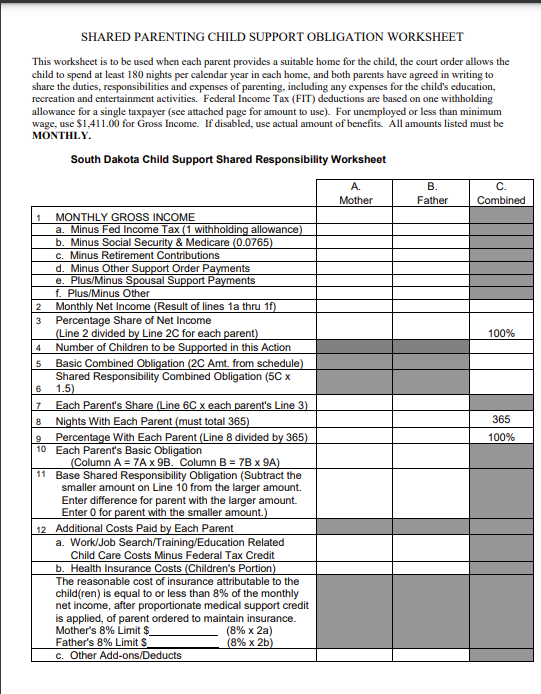
Step 1: use the child support calculator, download the South Dakota child support worksheet, or Shared Parenting Child Support Obligation Worksheet.

Step 2: compare the resulting figure to the economic table in the worksheet or Child Support Basic Obligation chart here. (see the snippet below).
What to remember:
- The calculator and worksheets only estimate support. Thus, the judge or DSS has the final say on how much you will pay.
- In split custody cases or if the parents agree to share parenting time equally, each parent may owe child support.
- The higher-earning parent often pays more.
- Gross income in the worksheet or calculator refers to all parental income(s) from all sources.
- The court will impute income if the parent is voluntarily unemployed or underemployed because a rebuttable presumption exists that assumes that a parent can work 35 hours per week on minimum wage even if he or she is behind bars.
South Dakota child support laws grounds for deviation
As mentioned, some situations might prompt the judge to deviate from south Dakota Child Support laws. For example, the child might need specialized education, or the resulting amount might be unfair to the paying parent.
What is important to remember is that the judge must explain his/her reason for deviating, so consult with a family court attorney in your area for better clarity.
How to modify child support in South Dakota
The circuit court is the only entity that has the authority to modify child support laws in South Dakota. The process begins with the petitioning parent filing a Petition for Modification Form at the local court.
From there, the Clerk of Court will review the request for completeness then advise you how to proceed.
What to remember:
- Your petition and all supporting attachments must be 8 ½ x 11 SIZE paper. If not, the Clerk of Court will reject your application.
- The petitioning parent must pay a $50 filing fee if he or she does not receive public assistance.
- You may request a fee waiver.
- If the petitioning parent does not appear in person or via telephone for a hearing, the referee tasked to conduct the modification hearing may dismiss the request.
- Parents may make voluntary out of court agreements before filing with the Clerk of Courts.
- Either parent may file objections contesting order changes within TEN days of the referee’s report.
- If you disagree with a court order, you may appeal the decision at the South Dakota Supreme Court within 30 days.
Overall, the modification process goes like this:
- File a petition at the DSS.
- DSS forwards the petition to the Clerk of Court.
- The court appoints a referee who schedules and conducts a hearing.
- Within 60 days, the referee mails you his/her recommendations.
At this stage, there exist only two possibilities. One is neither parent objects to the recommendations, and the court enters an order. Or either parent objects -and the court schedules a hearing.
Download instructions for filing a petition for modification of child support obligation here. Or call DCS at 605-773-3641.
You may also locate support service offices in your area here.
What happens if you do not pay child support in South Dakota?
Willful failure to pay child support is a crime in South Dakota that prompts the DCS to take the following enforcement actions.
- Income/wage withholding: the DCS may issue such orders requiring the paying parent’s employer to withhold not more than 50% of the payor’s income after mandatory deductions such as taxes and social security.
- Automatic withdrawal of income: instead of an income withholding order, the DCS may enter an alternative payment plan with the non-custodial parent.
- Credit bureau reporting: the DCS may report the delinquent parent to credit bureaus if you owe more than $1000 in back support.
- License suspension: the DCS may restrict your drivers, professional, or business license if you have not paid child support for three months or if you owe more than $1000.
- Passport denial: through the state department, the DCS may deny or revoke your passport if you owe at least $2500.
- Tax refund intercept: the DCS may also collect child support from federal, state, or local tax returns.
- The DCS may also withhold the paying parents’ assets held in banks and other financial institutions, lottery winnings, worker’s compensation, and all applicable lump-sum payments or benefits.
Contempt of court charges
Under South Dakota child support guidelines, parents may face Contempt of Court charges if the court finds that the caregiver has the ability or resources to pay but is willfully not paying.
In such a scenario, the DCS will escalate the case to a prosecutor who will set up “show cause hearings.” Thus, the accused will have the opportunity to defend his/her failure.
If the excuse for non-payment is valid, then the court may order modification or set up a payment plan.
Criminal non-payment south Dakota
If you move to another state to avoid paying child support, the judge may order 180 days in jail plus a fine. Also, South Dakota is one of the many States that allow the courts to add interest to child support arrears. Meaning, you may end up paying more than you owe.
At what age does child support end in South Dakota?
South Dakota child support laws require parents to pay upkeep until the child is 18. Additionally, your obligation may continue until the child’s 19th birthday if he or she is still in high school.
Also, your order may continue indefinitely if the child is severely mentally or physically disabled.
For parents worried about higher education expenses such as college or university, you may agree on a payment plan with your former partner. However, child support does not cover such expenses in South Dakota.
How to end child support early in South Dakota
South Dakota child support guidelines allow minors who are at least 16 years of age to petition for emancipation.
Apart from the age requirement, the minor must also show the court that he or she willingly lives independently from the parents, and the child’s income must be legal. You may also qualify for emancipation if you get married or join the US army.
Consult with a family court attorney to see if you qualify.
More South Dakota Laws