📑 Table of Contents (click to expand)
- Quick Summary: Alabama Child Support
- How is Child Support Calculated in Alabama?
- Understanding the Income Shares Model
- Alabama Child Support Guidelines Chart
- Shared Custody Rules (2023 Amendment)
- How to Modify Child Support
- Enforcement and Penalties
- When Does Child Support End?
- Establishing Paternity
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Additional Resources
Last verified: February 2026. Alabama child support guidelines are governed by Rule 32 of the Alabama Rules of Judicial Administration. The guidelines were last revised effective May 1, 2022, with the next quadrennial review scheduled to conclude by November 17, 2025.
Quick Summary: Alabama Child Support at a Glance
- Calculation Method: Income Shares Model (Rule 32)
- Governing Law: Alabama Rules of Judicial Administration, Rule 32
- Combined Income Range: Guidelines cover $0 to $20,000 per month combined gross income
- Age of Termination: 19 years old (Alabama’s age of majority)
- Enforcement Agency: Alabama Department of Human Resources, Child Support Enforcement Division
- Last Guidelines Update: May 1, 2022
- 2023 Amendment: New shared custody provisions for parents with approximately equal parenting time
How is Child Support Calculated in Alabama?
Alabama uses the “Income Shares Model” to calculate child support obligations under Rule 32 of the Alabama Rules of Judicial Administration. This model estimates how much parents would have spent on their children if the family had remained intact, then divides that amount between the parents based on their respective incomes.
The calculation process involves several steps:
- Determine gross monthly income for both the custodial and non-custodial parent
- Combine both parents’ gross incomes to find the total family income
- Refer to the Schedule of Basic Child Support Obligations to find the base support amount
- Calculate each parent’s percentage share based on their proportion of combined income
- Add adjustments for health insurance, daycare, and extraordinary expenses
Understanding the Income Shares Model
Under Rule 32(B), gross income includes virtually all income sources:
- Salaries, wages, and commissions
- Bonuses and overtime pay
- Self-employment income
- Severance pay
- Pensions and retirement benefits
- Interest and dividend income
- Trust income and annuities
- Capital gains
- Social Security benefits
- Workers’ compensation benefits
- Unemployment benefits
- Veteran benefits
- Gifts and prizes
Excluded from gross income: Public assistance benefits (TANF, food stamps, SSI) and child support received for children from other relationships.
Alabama Child Support Guidelines Chart
The Schedule of Basic Child Support Obligations (found in Appendix to Rule 32) provides the presumptive child support amount based on combined adjusted gross income and number of children. The chart covers combined monthly incomes from $0 to $20,000.
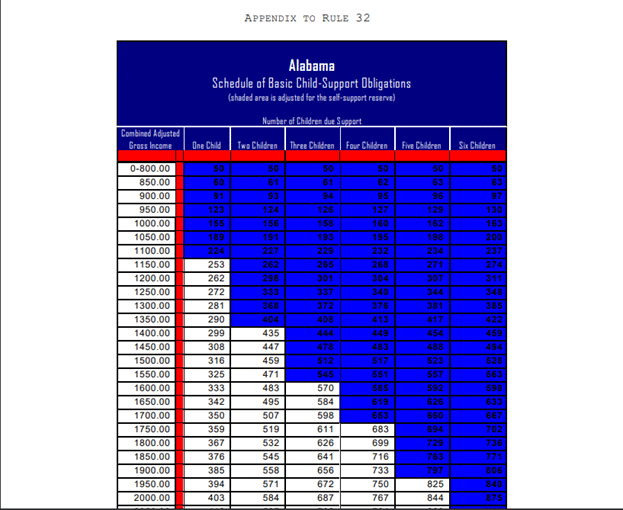
For combined gross incomes exceeding $20,000 per month, the court has discretion to determine an appropriate amount based on the children’s needs and the family’s standard of living.
Shared Custody Rules (2023 Amendment)
In 2023, Alabama amended Rule 32(C) to address shared custody situations. The shared custody calculation applies when both parents have custody approximately half of the time. This designation applies specifically to child support determination and recognizes that both parents incur direct expenses when the child is in their care.
Under the shared custody formula, the court considers:
- The number of overnights each parent has with the child
- Each parent’s income and proportional share
- Direct expenses each parent pays while the child is in their custody
How to Modify Child Support in Alabama
Either parent may petition to modify an existing child support order when there has been a material change in circumstances. Common grounds for modification include:
- Significant increase or decrease in either parent’s income
- Job loss or disability
- Changes in the child’s needs (medical, educational)
- Changes in custody arrangements
- Changes in the cost of health insurance or daycare
Under Alabama law, a difference of more than 10% between the current order and the amount calculated under the guidelines creates a rebuttable presumption that modification is warranted.
To request a modification, file a Petition for Modification with the circuit court that issued the original order. If you receive services through the Child Support Enforcement Division, you can request a review and adjustment through their office.
Enforcement and Penalties for Non-Payment
Failure to pay court-ordered child support in Alabama carries serious consequences. If a parent falls behind on payments, the custodial parent can file a motion for contempt of court.
Enforcement actions include:
- Wage garnishment: Automatic deductions from paychecks, unemployment benefits, or retirement benefits
- Credit bureau reporting: Arrears exceeding $1,000 are reported to credit agencies
- Passport denial: Arrears exceeding $2,500 result in passport denial, revocation, or restriction
- License suspension: Driver’s licenses, professional licenses, sporting licenses, and recreational licenses may be suspended
- Tax refund interception: State and federal tax refunds can be intercepted if arrears exceed $500
- Property liens: Liens may be placed on vehicles, real estate, and other valuable property
- Bank account levies: Funds can be seized directly from bank accounts
- Contempt of court: Willful non-payment can result in fines and jail time
“Contempt of court” applies when a parent willfully and purposely fails to pay. The legal remedy may include jail time, fines, or both. Parents who are 30 days or more behind on payments should seek legal counsel immediately.
When Does Child Support End in Alabama?
In Alabama, 19 is the age of majority, and child support typically terminates when the child turns 19. However, support may end earlier or continue longer in certain circumstances:
Child support may end before age 19 if:
- The child marries
- The child joins the military
- The child becomes legally emancipated
- The child dies
Child support may continue after age 19 if:
- The child has a physical or mental disability that prevents self-support
- The parents agreed to extended support (such as college expenses) in their divorce agreement
Important: Child support does not terminate automatically. The paying parent should file a motion to terminate support with the court when the child reaches the age of majority or when another terminating event occurs.
Establishing Paternity in Alabama
For unmarried parents, paternity must be established before a child support order can be entered against a father. Paternity can be established two ways:
- Voluntary acknowledgment: Both parents sign a CS-41 Affidavit of Paternity form. Once signed and filed, both parents’ names appear on the birth certificate.
- Court order: If parents cannot agree, either parent or the state can file a petition to establish paternity. The court may order genetic (DNA) testing, which is 99.9% accurate in determining biological parentage.
If you are uncertain about paternity, do not sign any acknowledgment forms or agree to support payments until paternity is established through DNA testing. Once paternity is established (voluntarily or by court order), it is extremely difficult to reverse.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does having another child affect my existing child support obligation?
No. Under Alabama law, having new children through remarriage, adoption, or a new relationship is considered a “voluntary” act and generally will not reduce your existing child support obligation. The court’s primary concern is ensuring support for children from the original relationship.
Can child support arrears be forgiven in Alabama?
Child support arrears can only be waived if the receiving parent signs a release of judgment. Even then, if the state paid public assistance on behalf of the child, the state’s portion of arrears cannot be waived. Arrears remain valid for many years, and collection efforts can continue even after the child reaches adulthood.
What if I cannot find the other parent?
The Child Support Enforcement Division can assist in locating absent parents through the State Parent Locator Service. This service searches DMV records, law enforcement databases, correctional facilities, state tax records, and employer databases.
Can the custodial parent withhold visitation if child support is not paid?
No. Visitation rights and child support are separate legal obligations. A custodial parent cannot legally withhold court-ordered visitation due to unpaid child support. Similarly, a non-custodial parent cannot refuse to pay support because visitation is being denied. Both issues should be addressed through the court.
What does child support cover in Alabama?
Child support is intended to cover the child’s basic needs, including housing, food, clothing, education, healthcare, dental care, entertainment, and extracurricular activities. The custodial parent is not required to provide receipts or account for how support is spent.
Additional Resources
Alabama Department of Human Resources, Child Support Enforcement Division
- Phone: (334) 242-9300
- Email: [email protected]
- Mailing Address: PO Box 304000, Montgomery, Alabama 36130-4000
Official Links:
- Rule 32: Alabama Child Support Guidelines (Official PDF)
- Alabama Child Support Guidelines Review Committee
If you need personalized legal advice about your child support case, consider consulting with a family law attorney in Alabama. Many attorneys offer free initial consultations.
More Alabama Laws